Snippet
""" Practice Memory Diagram """
x: int = 10
result: str = ""
while x >= 0:
if x % 3 > 0:
result = result + str(x)
else:
result = str(x) + result
x = x - 1
print(result)
Solution
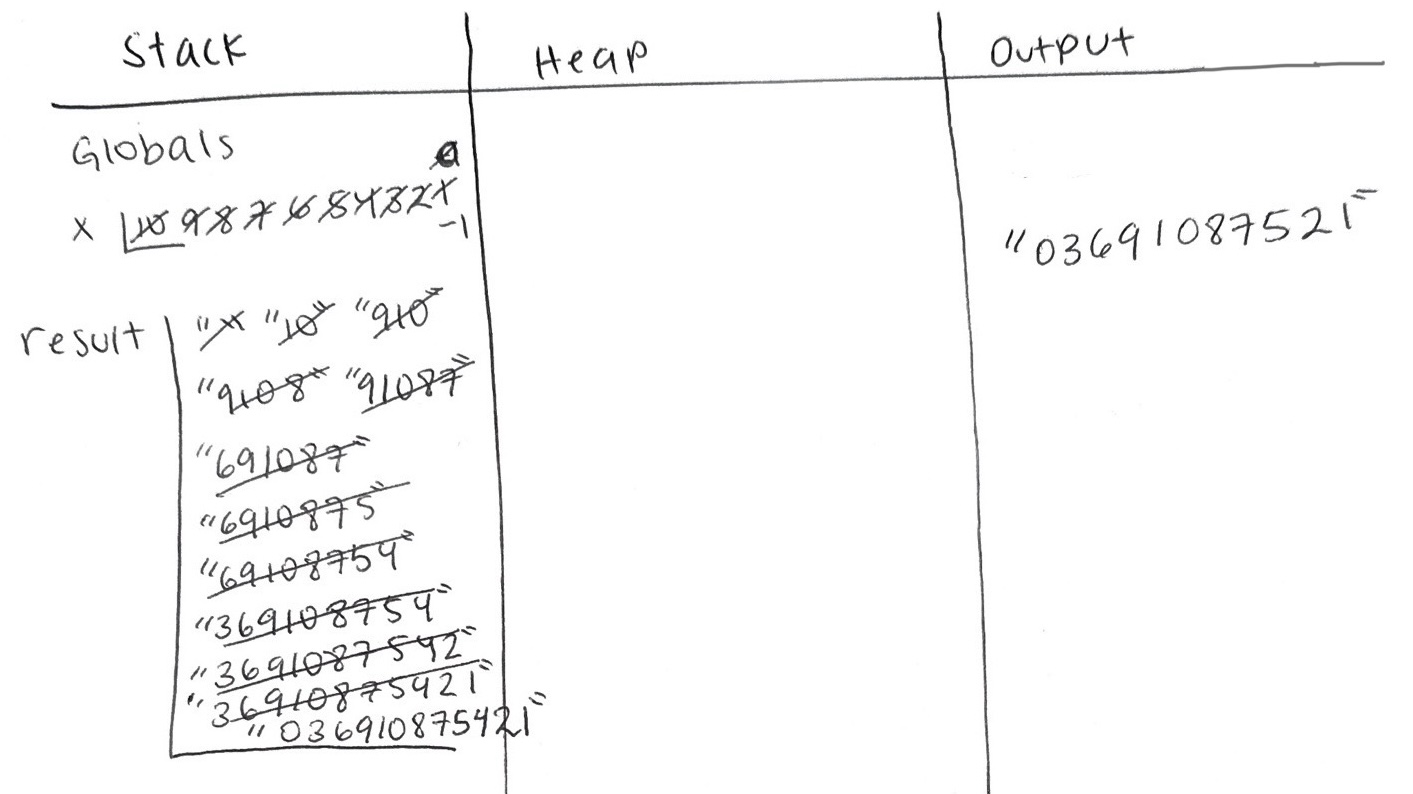
Image Description:
The memory diagram illustrates three columns: Stack on the left, Heap next to it, and Output beside the Heap. Within the stack, there are two variables: x and result. Initially, the value of x is set to the integer 10. It is then successively updated and crossed out to new values: 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, and finally -1 in which -1 is not crossed out. The variable result is initially assigned an empty string enclosed in two quotes. Subsequently, it undergoes updates and is crossed out to new values: 10, 910, 9108, 91087, 691087, 6910875, 69108754, 369108754, 3691087542, 36910875421, and concludes with a final value of 036910875421 where this final value is not crossed out.